|
A partir de 13/02/2025 esta página deixará de ser atualizada.
|
Glossário sobre Análise Gráfica
( A-C )
( D-F )
( G-J )
( K-M )
( N-S )
( T-Z )
- Daily Range
- The difference between the high and low price during one trading day.
- Debit Spread
- The difference in value of two options, where the value of the long position exceeds the
value of the short position.
- Deductive Logic
- Logic traditionally used in expert systems, which defines a method for reasoning from
the general to the specific.
- Deep-in-the-Money
- A deep-in-the-money call option has the strike price of the option well below the
current price of the underlying instrument. A deep-in-the-money put option has the strike
price of the option well above the current price of the underlying instrument.
- Degrees of Freedom
- The number of independent observations; the number of observations minus the number of
parameters to be estimated.
- Delay
- The amount of time that elapses between a change in an input event and the resultant
change in a related output event or time series.
- Delta
- The amount by which the price of an option changes for every dollar move in the
underlying instrument.
- Delta-Hedged
- An options strategy that protects an option against small price changes in the option's
underlying instrument. These hedges are constructed by taking a position in the underlying
instrument that is equal in magni tude but opposite in sign (+/-) to the option's delta.
- Delta Neutral
- This is an "options/options" or "options/underlying instrument"
position constructed so that it is rela tively insensitive to the price movement of the
underlying instruments. This is arranged by selecting a calculated ratio of offsetting
short and long positions.
- Delta Position
- A measure of option price vs. the underlying futures contract or stock price.
- Demand Index
- An index that shows the buying and selling power of markets and stocks from mathematical
calcu lations of volume and price ratios.
- Density Function
- For any measure m , a function that gives rise to m when integrated with
respect to some other specified measure. A probability density function is a function
whose integral over any set gives the probability that a random variable has values in
this set.
- Dependence
- A relationship between two different experimental results in which the first result does
not directly influence the chances of the second result occurring, but instead, the two
results are indirectly related because they are subject to influences from a common
outside factor.
- Derivatives
- Financial contracts the value of which depend on the value of the underlying instrument
commodity, bond, equity, currency or a combination.
- Deterministic
- Known in advance when the sum of one-step ahead forecast mean squared errors is zero.
- Deterministic
- The fundamental continuous effect of an exogenous variable such as money supply that can
be deter mined to be explanatory.
- Deterministic System
- A system in which the outcome is determined by an equation; a system in which cause and
effect is easily determined.
- Detrend
- To remove the general drift, tendency, or bent of a set of statistical data as related
to time.
- Difference-in-Means Test
- A statistical test that indicates the likelihood of observing the difference if the true
differ ence were zero. A large value of this statistic leads to nonacceptance of the null
hypothesis that the true difference is zero.
- Differencing
- Subtracting previous from current values to obtain a stationary (detrended) time series:
P stationary = Pt - Pt-1.
- Diffusion Equation
- A partial differential equation, used in solving a random walk problem.
- Diffusion Index
- An index that measures the percentage of individual series that are positive compared
with the aggregate group that is, the percentage of S&P groups that are above their
30-week moving average.
- Distribution
- Large monied interests use the current rally to liquidate old positions in the face of
good news.
- Distribution
- Any set of related values described by an average (that is, mean), which identifies its
midpoint, a measure of spread (that is, standard distribution) and a measure of its shape
(that is, skew or kurtosis).
- Divergence
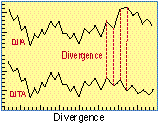
- When two or more averages or indices fail to show confirming trends.
- Doji
- A session in which the open and close are the same (or almost the same). Different
varieties of doji lines (such as a gravestone or long-legged doji) depend on where the
opening and close are in relation to the entire range. Doji lines are among the most
important individual candlestick lines. They are also components of important candlestick
patterns.
- Double Bottom (Top)
- The price action of a security or market average where it has declined (advanced) two
times to the same approximate level, indicating the existence of a support (resistance)
level and a possibility that the down ward (upward) trend has ended.
- Double-Smoothed
- A price series that has been smoothed by a mathematical technique such as a moving
average. This first series of smoothed price data is then smoothed a second time.
- Double Top
- See Double Bottom.
- Drawdown
- The reduction in account equity as a result of a trade or series of trades.
- Drunkard's Walk
- See Random walk.
- Durbin-Watson Statistic
- The probability that first order correlation exists. With a range between zero and 4,
the closer to 2.0, the lower the probability is.
- Dynamic Data Exchange
- Ability to automatically update an application from within another application.
- Early Entry
- A large price movement in one direction within the first 15 minutes after the open of
the daily session.
- Efficient Market Theory
- All known information is already discounted by the market and reflected in the price due
to market participants acting upon the information.
- Elasticity
- The ability to recover an original configuration.
- Elliott Wave Theory
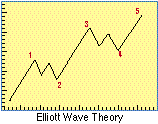
- A pattern-recognition technique published by Ralph Nelson Elliott in 1939, which holds
that the stock market follows a rhythm or pattern of five waves up and three waves down to
form a complete cycle of eight waves. The three waves down are referred to as a
"correction" of the preceding five waves up.
- EMA
- See Exponential Moving Average.
- Engulfing Pattern
- In candlestick terminology, a multiple candlestick line pattern; a major reversal signal
with two opposing-color real bodies making up the pattern. (Also referred to as tsutsumi.
)
- Envelope
- Lines surrounding an index or indicator that is, trading bands.
- Equilibrium Market
- A price region that represents a balance between demand and supply.
- Equivolume Chart
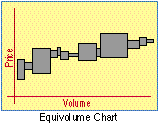
- Created by Richard W. Arms, a chart in which the vertical axis is the high-low range for
each day, while the horizontal axis represents the volume of shares of stock or the number
of contracts traded for the day. The purpose of the chart is to highlight the relationship
between price and volume.
- Estimated EPS Change
- (%) Change in estimated mean earnings for the current fiscal year from the last month,
last three months and last six months to the current month.
- Eurodollar
- Dollars deposited in foreign banks, with the futures contract reflecting the rates
offered between London branches of top US banks and foreign banks.
- Evening Star Pattern
- The bearish counterpart of the morning star pattern; a top reversal, it should be acted
on if it arises after an uptrend.
- Ex-Dividend Date
- The day on or after which the right to receive a current dividend is not automatically
transferred to a buyer.
- Exercise
- The process by which the holder of an option makes or receives delivery of shares of the
underlying secu rity.
- Expert Systems
- Dynamic but not adaptable, expert systems are rule-driven systems that cannot learn as
the result of new information being fed into its system as opposed to neural networks,
which can.
- Expiration
- The last day on which an option can be traded.
- Explained
- The relative reduction in the variation of variable Y that can be attributed to a
knowledge of variable X and its relationship to Y.
- Exponential Moving Average
- The EMA for day D is calculated:
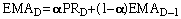 as where PR is the price on day D and a (alpha) is a smoothing
constant: as where PR is the price on day D and a (alpha) is a smoothing
constant: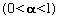 . Alpha
may be estimated as 2/(n+1), where n is the simple moving average length: . Alpha
may be estimated as 2/(n+1), where n is the simple moving average length: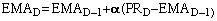 . .
- Exponential Smoothing
- A mathematical-statistical method of forecasting that assumes future price action is a
weighted average of past periods; a mathematic series in which greater weight is given to
more recent price action.
- Expert Systems
- Dynamic but not adaptable, expert systems are rule-driven systems that cannot learn as
the result of new information being fed into its system as opposed to neural networks,
which can. Most successful in financial applications where governing rules are consistent.
- Extreme
- The highest or lowest price during any time period, a price extreme; in the CBOT Market
Profile, the highest/lowest prices the market tests during a trading day.
- F Statistics
- The ratio of the variance explained by treatments to the unexpected variance.
- Fade
- Selling a rising price or buying a falling price. A trader fading an up opening would be
short, for example.
- Failure Swings
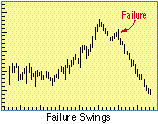
- The inability of price to reaffirm a new high in an uptrend or a new low in a downtrend.
- Failure
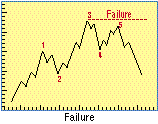
- In Elliott wave theory, a five-wave pattern of movement in which the fifth impulse wave
fails to move above the end of the third, or in which the fifth wave does not contain the
five subwaves.
- Fair Values
- The theoretical prices generated by an option pricing model (i.e. , the
Black-Scholes option pricing model).
- Fast Fourier Transform
- A method by which to decompose data into a sum of sinusoids of varying cycle length,
with each cycle being a fraction of a common fundamental cycle length.
- Fast Market
- A declaration that market conditions in the futures pit are so disorderly temporarily to
the extent that floor brokers are not held responsible for the execution of orders.
- Feedforward Computation
- Neural network in which neurons receive information only from the previous layer and
send outputs only to the following layer.
- Fibonacci Ratio
- The ratio between any two successive numbers in the Fibonacci sequence, known as phi
(f). The ratio of any number to the next higher number is approximately 0.618 (known as
the Golden Mean or Golden Ratio), and to the lower number approximately 1.618 (the inverse
of the Golden Mean), after the first four numbers of the series. The three important
ratios the series provides are 0.618, 1.0 and 1.618.
- Fibonacci Sequence
- The sequence of numbers (0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233...), discovered
by the Italian mathematician Leonardo de Pisa in the 13th century and the mathematical
basis of the Elliott wave theory, where the first two terms of the sequence are 0 and 1
and each successive number in the sequence is the sum of the previous two numbers.
Technically, it is a sequence and not a series.
- Fill
- An executed order; sometimes the term refers to the price at which an order is executed.
- Fill Order
- An order that must be filled immediately (or canceled).
- Filter Point
- The time at which a portfolio insurance program makes an adjusting trade.
- Filter
- A device or program that separates data, signal or information in accordance with
specified criteria.
- Fire
- (verb) In expert system programming, ordinarily used to describe the
"triggering" or "activation" of a rule. A rule is "fired,"
"triggered" or "activated" when its conditions have been met, and its
"consequents" (resultant facts) are added to the knowledge base.
- Fit Criterion
- A quantitative comparable measure used to minimize model errors.
- 5% Confidence
- Before conducting statistical tests, an analyst must select a confidence level that will
be used to determine when to accept the null hypothesis. A 5% confidence level indicates
that one is not willing to accept the null hypothesis when the average net return
calculated from the sample could have occurred in only five of 100 samples if the null
hypothesis were true.
- Flaglike
- Sideways market price action that has a slight drift in price counter to the direction
of the main trend; a consolidation phase.
- Float
- The number of shares currently available for trading.
- Floor Traders
- Employees of brokerage firms working on exchange trading floors.
- Flyers
- Speculative or high-risk trades.
- Forecast Origin
- The most recent historical period for which data is used to build a forecasting model.
The next time period is the first forecast period.
- Forward-Rate Agreements (FRAs)
- Cash payments are made daily as the spot rate varies above or below an agreed -upon
forward rate and can be hedged with Eurodollar futures.
- Fractal Dimension
- From fractal geometry, used to describe the irregular nature of lines, curves, planes or
volumes.
- Fractals
- Depiction of mathematical models that may be applied to identify data patterns.
- Frequency
- The number of complete cycles observed per time period (i.e., cycles per year).
- Frequency Component
- That part of a time series that may be represented as a cycle.
- Frequency Distribution
- A chart showing the number of times (or "frequency") an event occurs for each
possible value of the event. The vertical or y-axis of the chart is the frequency axis and
the horizontal or x-axis shows the different values the variable being measured can take.
- Frequency Domain
- Variation in a time series is accounted for by cyclical components at different
frequencies.
- Frequency Response
- The transfer of the frequency of the underlying data, usually prices, to the frequency
of its moving average.
- Front-Loaded
- Commission and fees taken out of investment capital before the money is put to work.
- Front Month
- The first expiration month in a series of months.
- Fundamental Analysis
- The analytical method by which only the sales, earnings and the value of a given
tradable's assets may be considered.
- Fundamentals
- The theory that holds that stock market activity may be predicted by looking at the
relative data and statistics of a stock as well as the management of the company in
question and its earnings.
- Future Volatility
- A prediction of what volatility may be like in the future.
- Fuzzy Systems
- A problem-solving method that can be applied to neural networks, expert systems and
other comput ing methods. Fuzzy systems process inexact information inexactly and describe
ambiguity rather than the uncer tainty of an occurrence and are useful in performing
control and decision-making tasks. Not Boolean.
( A-C )
( D-F )
( G-J )
( K-M )
( N-S )
( T-Z )
|