|
A partir de 13/02/2025 esta página deixará de ser atualizada.
|
Glossário sobre Análise Gráfica
( A-C )
( D-F )
( G-J )
( K-M )
( N-S )
( T-Z )
- Gamma
- The degree by which the delta changes with respect to changes in the underlying
instrument's price.
- Gann's Square of 9
- A trading tool that relates numbers, such as a stock price, to degrees on a circle.
- Gap
- A day in which the daily range is completely above or below the previous day's daily
range.
- Genetic Algorithms
- Algorithms that mimic the characteristics associated with evolution and that are
well-suited to optimization problems such as optimizing neural network parameters.
- Genetic Programming
- In artificial intelligence, this form of programming automatically generates a program
from a set of primitive constructs.
- Give-up
- When a broker executes an order for another broker's client and the two brokers split
the commission; the client pays nothing extra.
- Golden Mean or Golden Ratio
- The ratio of any two consecutive numbers in the Fibonacci sequence, known as phi and
equal to 0.618; a proportion that is an important phenomenon in music, art, architecture
and biology.
- Golden Section
- Any length divided so that the ratio of the smaller to the larger part is equivalent to
the ratio between the larger part and the whole and is always 0.618.
- Growth Fund
- A more speculative mutual fund made up primarily of the growth or performance stocks
that are expected to appreciate in price more than the broad market over an extended time
period.
- Guaranteed Investment Contracts (GICs)
- A single lump-sum deposit that earns a guaranteed interest until a known maturity date.
GICs are issued by insurance companies.
- Hanning Weight
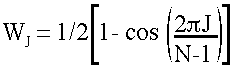
where weight (W) at point J in window width of N points is determined by this formula.
- Harami
- In candlestick terminology, a small real body contained within a relatively long real
body.
- Heuristic Method
- Problem solving approached by trying out several different methods and comparing which
pro vides the best solution.
- Heuristics
- (computer science)Computational rules of thumb. Distinct from algorithms, which are
programs guaran teed to generate the correct result under all circumstances, heuristics
may only turn out to be correct a certain percentage of time.
- Hidden node
- Elements that give a neural network the ability to learn nonlinear patterns. The hidden
nodes math ematically transform inputs by passing weighted sums of those inputs through
nonlinear functions.
- Hierarchical Neural Network
- In artificial intelligence, a neural network in which predictions derived from networks
at one level of the hierarchy are incorporated as inputs at another level. This
architecture lends itself to faster training, as each network focuses learning solely on
its own output.
- High Pass Frequency Filter
- A detrending filter that lets pass the high frequency noise and rejects low frequency
trend. Implemented by first applying a low pass filter to the data, then subtracting the
filtered data from the original data.
- High-Ticking
- To pay the offered price.
- Hines Ratio
- A modified put/call ratio that refines traditional option ratio analysis by including
the open interest figures in the equation and can be defined as (Total put volume/Total
put open interest) divided by (Total call volume/Total call open interest)
- Historic Volatility
- How much contract price has fluctuated over a period of time in the past; usually
calculated by taking a standard deviation of price changes over a time period.
- Historical Data
- A series of past daily, weekly or monthly market prices (open, high, low, close, volume,
open inter est).
- Hook Day
- A trading day in which the open is above/below the previous day's high/low and the close
is below/above the previous day's close with narrow range.
- Implied Alpha
- The excess return expected from a stock to justify its current weighing in the
portfolio.
- Implied Volatility
- The volatility computed using the actual market prices of an option contract and one of
a number of pricing models. For example, if the market price of an option rises without a
change in the price of the underlying stock or future, implied volatility will have risen.
- Impulse
- A sharply defined change in a series of input data being studied, such as market prices
or volume.
- Impulse Wave
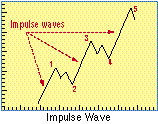
- A wave or cycle of waves that carries the current trend further in the same direction.
- In Play
- A stock that is the focus of a public bidding contest, as in a takeover or bear raid.
- In-the-Money
- A call option whose strike price is lower than the stock or future's price, or a put
option whose strike price is higher than the underlying stock or future's price. For
example, when a commodity price is , a call option with a strike price of is
considered in-the-money.
- Income Dividends
- Payments to mutual fund shareholders consisting of dividends, interest and short-term
capital gains earned on the fund's portfolio securities after deduction of operating
expenses.
- Inductive Logic
- The progress from statements describing particular events to a general statement.
- Initial Balance
- The first or first two half-hour trading periods in the CBOT Market Profile during which
prices tend to converge; the initial auction of the trading day.
- Inside Day
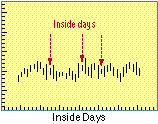
- A day in which the daily price range is completely within the previous day's daily price
range.
- Interest Rate Swaps
- An arrangement that requires both sides of the transaction to make payments to each
other based on two different interest rates. The most commonly traded requires one side to
pay a fixed rate and the other to pay a floating rate.
- Intermarket Analysis
- Observing the price movement of one market for the purpose of evaluating a different
market.
- Intrinsic Value
- The portion of an option's premium that is represented when the cash market price is
greater than the exercise price; a known constant equal to the difference between the
strike price and underlying market price.
- Irregular Flat
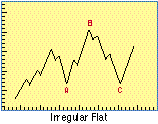
- A type of Elliott wave correction that has a 3-3-5 wave pattern, where the B wave
terminates beyond the start of wave A. A "flat" is in progress, implying that a
larger pattern is developing. It will contain waves of one
higher degree than the A-B-C waves just completed.
- January Effect
- The tendency for securities prices to recover in January after tax-related selling is
completed before the year-end.
( A-C )
( D-F )
( G-J )
( K-M )
( N-S )
( T-Z )
|